What is chess all about?
History:-
chess is originated from India.can be traced back nearly 1500 years; From India, the game spread to Persia. When the Arabs conquered Persia, chess was taken up by the Muslim world and subsequently spread to Southern Europe. In Europe, chess evolved into roughly its current form in the 15th century.
605 million adults play chess regularly". Chess is played at least once a year by 12% of British people, 15% of Americans, 23% of Germans, 43% of Russians, and 70% of Indian people.

Setup:-
Chess is a two-player strategy board game played on a chessboard, a checkered game board with 64 squares arranged in an 8×8 grid.
Each player begins with 16 pieces: one king, one queen, two rooks, two knights, two bishops, and eight pawns. Each of the six piece types moves differently,
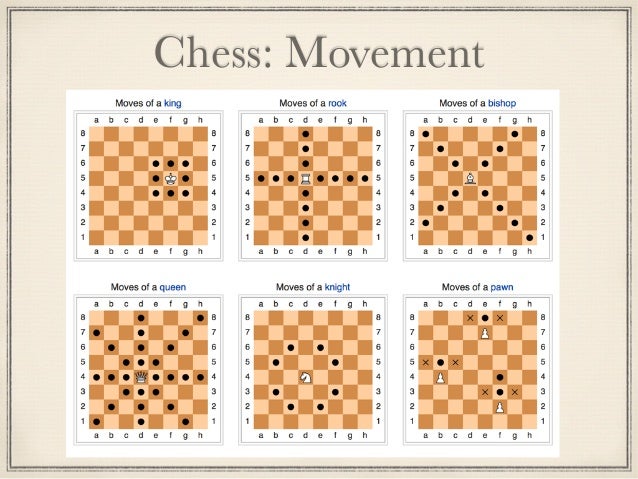
Movement:-
The player with the white pieces always moves first. If the player to move has no legal move, the game is over; it is either a checkmate or stalemate!
- The king moves one square in any direction. The king also has a special move called castling that involves also moving a rook.
- The rook can move any number of squares along a row(rank) or column(file), but cannot leap(jump) over other pieces. Along with the king, a rook is involved during the king's castling move.
- The bishop can move any number of squares diagonally, but cannot leap over other pieces.
- The queen combines the power of a rook and bishop and can move any number of squares along a row, column, or diagonal, but cannot leap over other pieces.
- The knight moves an "L"-shape: two squares vertically and one square horizontally, or two squares horizontally and one square vertically.
- The knight is the only piece that can leap over other pieces.
- The pawn can move forward to the unoccupied or the pawn can capture an opponent's piece on a square diagonally on an adjacent file, A pawn has two special moves: the en passant capture and promotion.
Castling:-
Castling consists of moving the king two squares along the first rank toward a rook
Castling is permissible under the following conditions
- Neither the king nor the rook has previously moved during the game.
- There cannot be any pieces between the king and the rook.
- The king cannot be in check, nor can the king pass through squares that are under attack by enemy pieces, or move to a square where it would result in a check. Note that castling is permissible if the rook is attacked, or if the rook crosses a square that is attacked.
En Passant:-
When a pawn advances two squares from its starting position and there is an opponent's pawn on an adjacent file next to its destination square, then the opponent's pawn can capture it en passant (in passing), and move to the square the pawn passed over. This can only be done on the very next move, otherwise, the right to do so is forfeit.
Promotion:-
When a pawn advances to the eighth rank, as a part of the move it is promoted and must be exchanged for the player's choice of queen, rook, bishop, or knight of the same color.
Check:-
When a king is under immediate attack by one or two of the opponent's pieces, it is said to be in check.

End of game:-
"Win"
Games can be won in the following ways:
- Checkmate,
- Resignation,
- Win on time.
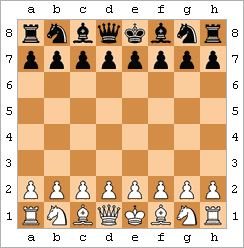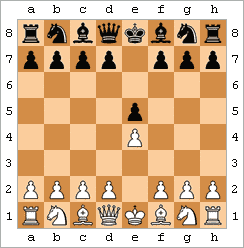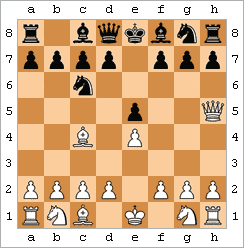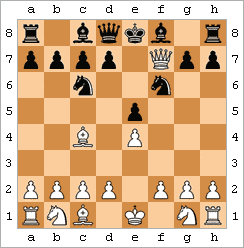
"Draw"
There are several ways games can end in a draw:
- Draw by agreement: mutual agreement between the players.
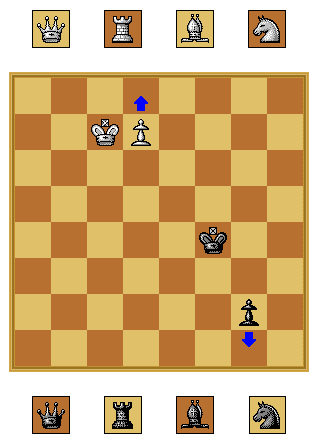
- Stalemate:- no legal move and is not in check. shown in the figure.
- three-time repetition of the same move
- Fifty-move rule: 50 moves and no pawn has been moved and no capture has been made, either player can claim a draw.
- Draw on time: In games with a time control, the game is drawn if a player is out of time and the opponent has no theoretical possibility to checkmate the player.
Notation and Recording:-
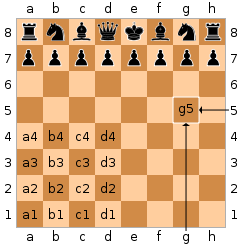
Examples of Indication,
Qg5 means "queen moves to the g-file and the 5th rank".
Ngf3 means "knight from the g-file moves to the square f3".
R1e2 means "rook on the first rank moves to e2".
The letter P for a pawn is not used so that e4 means "pawn moves to the square e4".
Pawn achieving promotion, e1Q or e1=Q.
Castling, 0-0 for kingside castling and 0-0-0 for queenside castling.
Check, "+" added. (The notation "++" for a double check is considered obsolete.)
Checkmate can be indicated by "#". At the end of the game,
"1–0" means "White won", "0–1" means "Black won", and "½–½" indicates a draw.
This is all about chess by basics! hope it is simple to understand. Thank you! :-)
Let us see a very nice game by Richard Reti:-
You can be in touch with me via:
Mail: shamji.jethva97@gmail.com
fb: https://www.facebook.com/shashvat.jethva
Mail: shamji.jethva97@gmail.com
fb: https://www.facebook.com/shashvat.jethva

Comments
Post a Comment